|
|
+ Home | ||

|
||||
| + Solar Cycle Prediction | + Magnetograph | + The Sun in Time | + The Hinode Mission | + The STEREO Mission |
The Solar Maximum Mission
|
The Solar Maximum Mission (SMM or SolarMax) was launched on February 14, 1980. It carried several scientific instruments which provided new insights into the nature of solar flares. The spacecraft was rescued and repaired by a 1984 Space Shuttle Challenger mission. This rescue and repair of SMM, (153 kb GIF image) , (124 kb GIF image) , (133 kb GIF image) , extended the useful lifetime of the mission to allow for better coverage of the solar activity cycle. SMM reentered the Earth's atmosphere and burned-up on December 2, 1989. SMM carried a battery of instruments designed to study solar flares and the active solar atmosphere. These instruments included the Ultraviolet Spectrometer and Polarimeter (UVSP), the Active Cavity Radiometer Irradiance Monitor (ACRIM), the Gamma-Ray Spectrometer (GRS), the Hard X-Ray Burst Spectrometer (HXRBS), the soft X-Ray Polychromator (XRP), the Hard X-ray Imaging Spectrometer (HXIS), and the Coronagraph Polarimeter (CP). | ||
|
Several members of the MSFC Solar Physics Group were involved with UVSP under the direction of Dr. Einar Tandberg-Hanssen. UVSP was designed to study the ultraviolet radiation emitted by the Sun in flares, active regions, and prominences. It was capable of acquiring simultaneous images in four different spectral positions as it scanned across the Sun. A rotating polarizer was used to measure magnetic fields as well. | |||
|
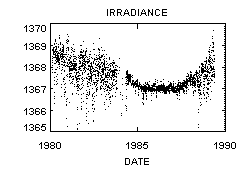
The ACRIM instrument package monitored the total energy output of the Sun (often referred to as the "Solar Constant") throughout the mission with great precision. These observation showed the expected dimming of the Sun when sunspots rotated into view and provided important information on the extent of this dimming. More importantly, however, ACRIM showed that the Sun is actually brighter during the maximum of the sunspot cycle when more spots are observed on the Sun's surface. Although the sunspots themselves are dark and produce dimming, they are surrounded by faculae that are bright and, on average, more than offset the dimming due to the sunspots. | ||
|
The HXIS instrument obtained images over small areas of the sun within six energy bands from 3.5 to 30 keV (3.5 to 0.4Å). The central part of the images had a spatial resolution of 8 arc-seconds. The normal time resolution was about 8 seconds but some flare observations were obtained with 1.5 second time intervals. HXIS observations showed that energetic X-rays are emitted from the footpoints of the magnetic loops seen in solar flares. HXIS showed that large coronal loops with temperatures up to 10 million degrees Kelvin are probably always present in the corona. HXIS also found that X-rays are often seen from widely separated point prior to the onset of a coronal mass ejection. The GRS instrument had three detector systems that together measured the spectra of flare X-rays and gamma rays with energies from 14keV to 140 MeV. These observations showed that gamma ray emission from even modest flares was fairly common and that particles are accelerated in flares to high energies in just a few seconds. | |||